01
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide, and the age of onset is mostly 30-60 years old. In 2020, there will be about 110,000 new cases of cervical cancer in China, and about 59,000 deaths, which is equivalent to one woman being diagnosed with cervical cancer every 5 minutes, and one woman dying of cervical cancer every 9 minutes.
However, cervical cancer is a malignant tumor with effective means of prevention. Nowadays, due to the promotion and popularization of cytological examination of cervical cancer exfoliation, many precancerous lesions and early cancers have been detected and prevented early, invasive cancer has been significantly reduced, and the five-year survival rate and cure rate have been significantly improved.
02
Symptoms of cervical cancer
Symptoms of early cervical cancer may include:
· Irregular blood spots or mild bleeding in women of childbearing age between periods;
· Blood spots or bleeding after menopause;
· Bleeding after intercourse;
· Increased vaginal discharge, sometimes smelly.
As cervical cancer progresses, more severe symptoms occur, including:
Persistent back pain, leg pain and/or pelvic pain;
· Weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite;
· Vaginal discomfort and odor of secretions;
· Swelling of one leg or both lower limbs.
More severe symptoms can occur in later stages, depending on which organs the cancer has metastasized to. (World Health Organization website)
03
What causes cervical cancer?
The etiology and pathogenesis of cervical cancer are not fully understood, and it is generally believed that it is related to many factors such as early marriage, fertility, cervical laceration, local poor hygiene, and foreskin stimulation. Epidemiological investigation found that premature sexual life and sexual disorder are high risk factors for cervical cancer (both men and women). Sexually transmitted HPV infection may be the main pathogenic factor of cervical cancer. HPV coding proteins E6 and E7 can inactivate p53 and Rb tumor suppressor genes, change cell cycle and DNA repair, induce genomic instability, and eventually lead to uncontrolled proliferation of normal cervical epithelial cells and malignant transformation.
04
Prevention of cervical cancer two magic weapon
1. Get the HPV vaccine early
HPV vaccination is one of the effective ways to prevent cervical cancer. At present, imported 2-valent, 4-valent and 9-valent HPV vaccines and domestic 2-valent HPV vaccines have been listed in China.
HPV vaccines target high-risk human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, the main types of viruses that cause cervical cancer. Because the HPV vaccine has a cross-protective effect, if conditions are limited, you can choose to vaccinate the 2-valent or 4-valent HPV vaccine first to prevent cervical cancer. When conditions permit, the 9-valent HPV vaccine should be supplemented.
2. Get regular HPV and TCT tests
In cervical cancer screening, HPV and TCT are the most commonly used tests. TCT tests are used to see if the cells in the cervix are diseased, while HPV tests are used to detect the presence of a foreign virus.
In the "Cancer Prevention and Screening Guidelines" issued by the National Health Commission in 2021, it is recommended that the starting age of screening for sexually active or married women is 25-30 years old, and cytological TCT examination is performed every three years. Hiv-infected women or women with low immune function can advance as appropriate.
Both of these tests are not 100% sure that they can detect the lesion infection, and both may have a 10%-20% missed diagnosis rate, so if you want to do cervical cancer screening, it is best to do HPV and TCT together.
Compared with the traditional Pap smear, TCT can significantly improve the detection rate of abnormal cervical cells. At the same time, it can also find some precancerous lesions, microbial infections such as mold, trichomonas, viruses, chlamydia and so on. At present, Beant TCT cervical cytology test kit is now on sale, welcome dealers to come to inquire, together to help cervical cancer patients early detection, early diagnosis, early treatment.
05
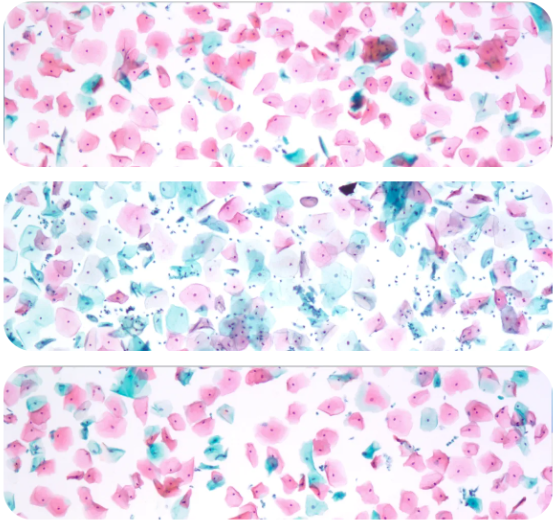
Beant TCT cervical cytology test kit
Dyeing effect